It’s been two weeks since I returned from Aotearoa New Zealand where I was attending the overlapping International Society for Contemporary Music (ISCM) World New Music Days and Asian Composers League festivals in Tāmaki Makaurau Auckland and Ōtautahi Christchurch. But given all the things I’ve plunged into since returning, while fighting jetlag from the 16-hour time difference and the grueling 27 1/2-hour door-to-door journey back to New York City, I still haven’t been able to completely wrap my brain around everything I experienced during the 12 days I was there.
First, a little background. Part of my work for New Music USA, in my role as Composer Advocate, is to advocate for our programs and values both nationally and internationally through various member-based networks, such as the ISCM and the International Association of Music Centres (IAMIC). Prior to the global pandemic, the members of these networks met annually to compare practices for supporting and advocating for music as well as to share music with each other. ISCM meetings occur in a different city somewhere in the world every year concurrently with a multi-concert festival called the World (New) Music Days (WNMD) which features music from each of the countries represented in the network. (The “New” is in parenthesis since some hosts call the festival simply “World Music Days.”) Since 2019, I have served on the boards of both organizations but, since the pandemic, that has meant meeting on Zoom often at less than optimal hours (sometimes at 6:00 A.M. or after Midnight for me) to accommodate the time zones of all the participants. However, in May, IAMIC held its first in-person conference in three years, which took place in multiple cities in Germany (Hamburg, Bonn, and Cologne). And in August, the ISCM finally convened in New Zealand for the first time, an event that had originally been scheduled for April 2020. (Before I was elected to ISCM’s Executive Committee, I wrote several very detailed reports of these annual festivals; to get a better sense of what a WNMD is like, you might enjoy reading the last of these, my account of the 2016 Festival in Tongyeong, South Korea, in which I attempted to explain the cultural milieu of the ISCM by comparing it to the Wizarding world as described in the Harry Potter novels.)
My trip to Germany in May for the 2022 IAMIC Conference was the first time I had left the country since the pandemic, and I was filled with anxiety a great deal of the time. But aside from the discomfort of wearing a mask everywhere including on a long overnight flight, the suitcase containing clothing I had brought for the trip not catching up with me until the night before I flew back home (which offered me an experience I otherwise never would have had of very quickly shopping for overpriced poorly fitting clothing in a Hamburg department store–don’t ask), and one of the delegates getting COVID (thankfully everyone diligently tested every day and it didn’t spread further), it was an extremely worthwhile week. I am particularly proud of a panel I moderated at the Beethoven-Haus in Bonn which focused on the extremely generous pandemic-era funding for creative artists based in Germany which made the delegates attending from everywhere else in the world extremely envious.
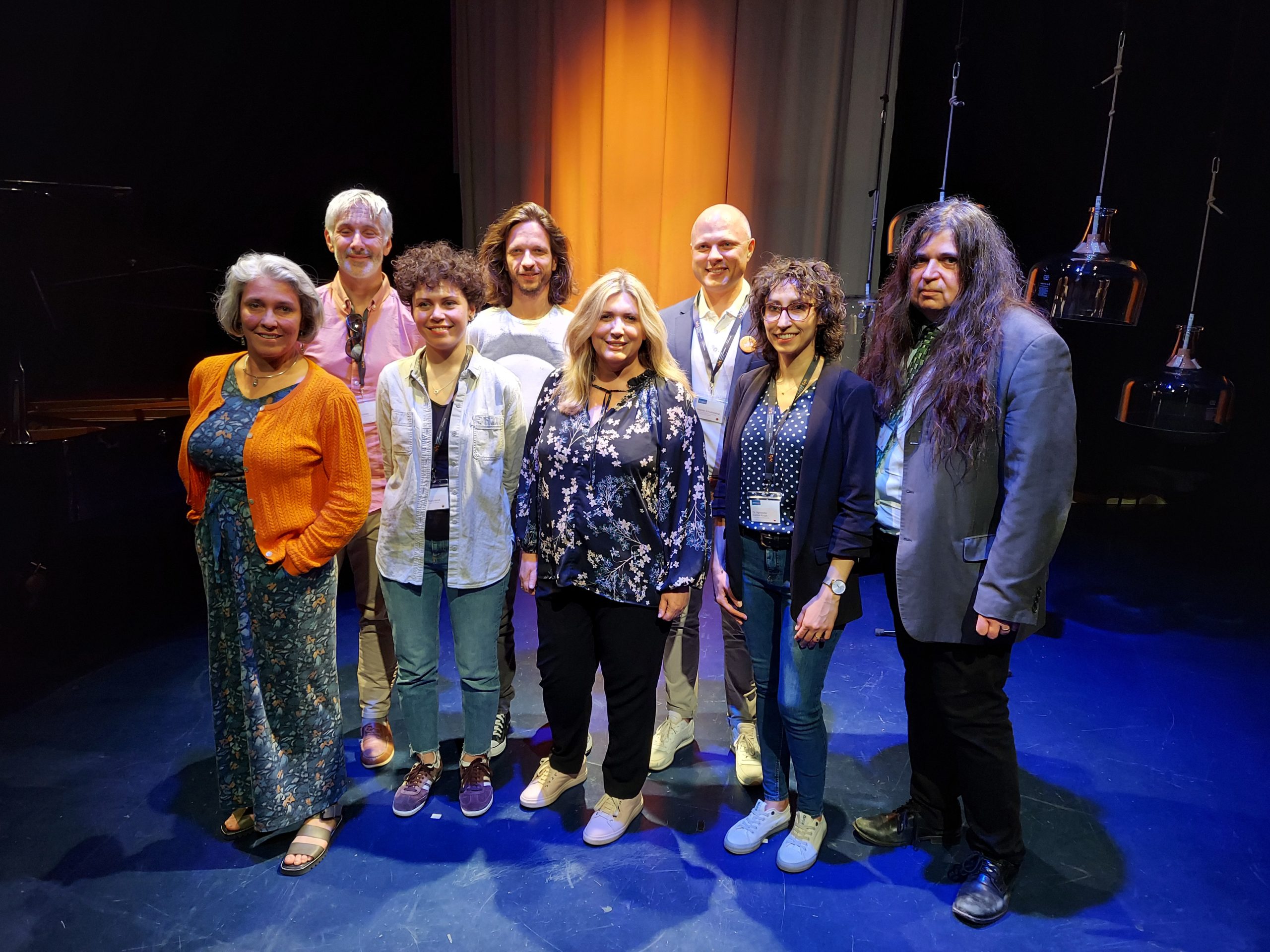

The IAMIC Board of Directors at the headquarters of Ensemble Musikfabrik in Cologne, Germany in May 2022. Pictured left to right are Deborah Keyser, Jonathan Grimes, Radvilė Buivydienė, Peter Baros, Diana Marsh, Stephan Schulmeistrat, Agnieszka Cieślak-Krupa, and FJO. (Note the replicas of Harry Partch’s Cloud Chamber Bowls on the far right.)
By the time August rolled around and I journeyed to New Zealand, I was a seasoned pandemic traveler. But nothing (not even having travelled there once before, 15 years ago, for a IAMIC conference) is sufficient physical or psychological preparation for a flight from the West Coast of North America across the Pacific Ocean and far down into the Earth’s other hemisphere to finally reach Auckland. It’s a 13-hour flight that, if coming from NYC, must be proceeded by a 6-hour flight to get to the West Coast as well as a massive trek between terminals which, even though there’s a more than two-hour layover, is a race against the clock, made even more challenging when masked. (In September, now that I’m back, Air New Zealand just introduced a brand new direct New York JFK-Auckland flight which lasts nearly 18 hours, though I’m not sure whether a direct flight or two long flights with a very long walk in between is worse.)
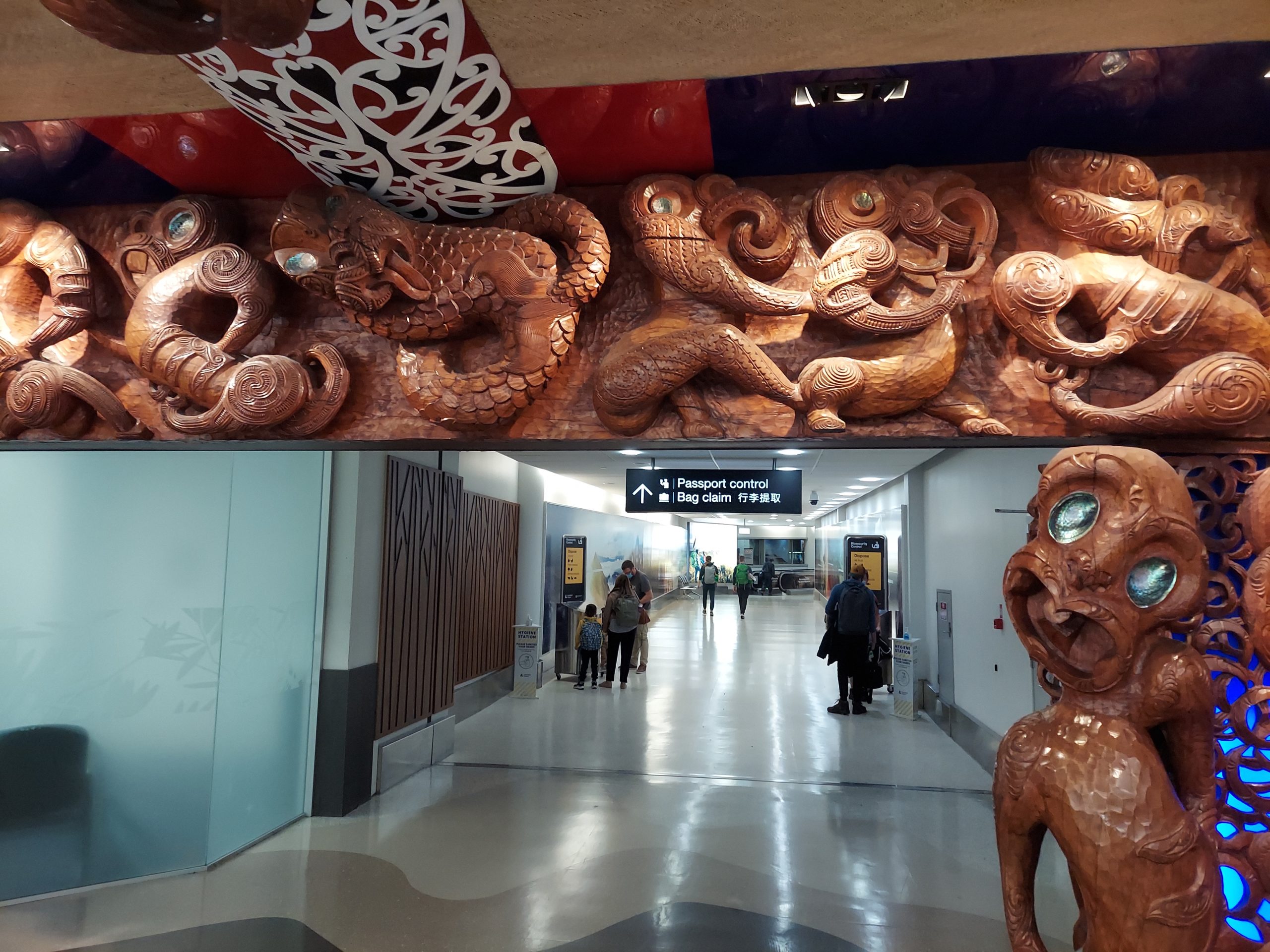

Among the first things visitors see after arriving in the Auckland Airport after an extremely long international flight. (They also pipe in a recording of Maori traditional chants.)
Before I continue, I’d like to offer a small disclaimer. Given the role I now have within ISCM, it seems somewhat of a conflict of interest for me to be singing the praises of the World New Music Days in an expansive report, so this should not be construed as that. Nevertheless, it seems appropriate to offer some information here on each of the American pieces that were performed, offer a few observations about what made this particular edition unique (especially since it is the first one that took place in more than three years), and to give readers here a sense of what I’ve been up to recently.
Although it had to be somewhat scaled down from what had originally been planned for 2020, the 2022 ISCM World New Music Days, which took place concurrently with a festival of the Asian Composers League, was a major undertaking that seemed to happen through sheer force of will, mainly on the part of the festival’s Artistic Director, Glenda Keam, who also happens to be the President of ISCM. All in all, 20 of the submitted works that had originally been chosen for performance (among them, sadly, Katherine Balch‘s extraordinary string quartet drip music which was a submission from the League of Composers, the official ISCM USA Section), could not be presented this year, plus two additional works listed in the program (that were not from ISCM submissions) had to be cancelled. In addition, due to the ongoing uncertainties of the global pandemic, many delegates could not attend (our general assembly meetings were an often challenging hybrid of in-person and Zoom), so many of the concerts were not as well attended as they should have been. Still, as in previous editions of the WNMD, the festival offered a fascinating cross section of music by composers hailing from six continents. (Despite a fascinating exhibit devoted to Antarctic exploration in the Canterbury Museum, which was around the corner from some of the concerts in Christchurch, a viable new music scene has yet to develop there.)
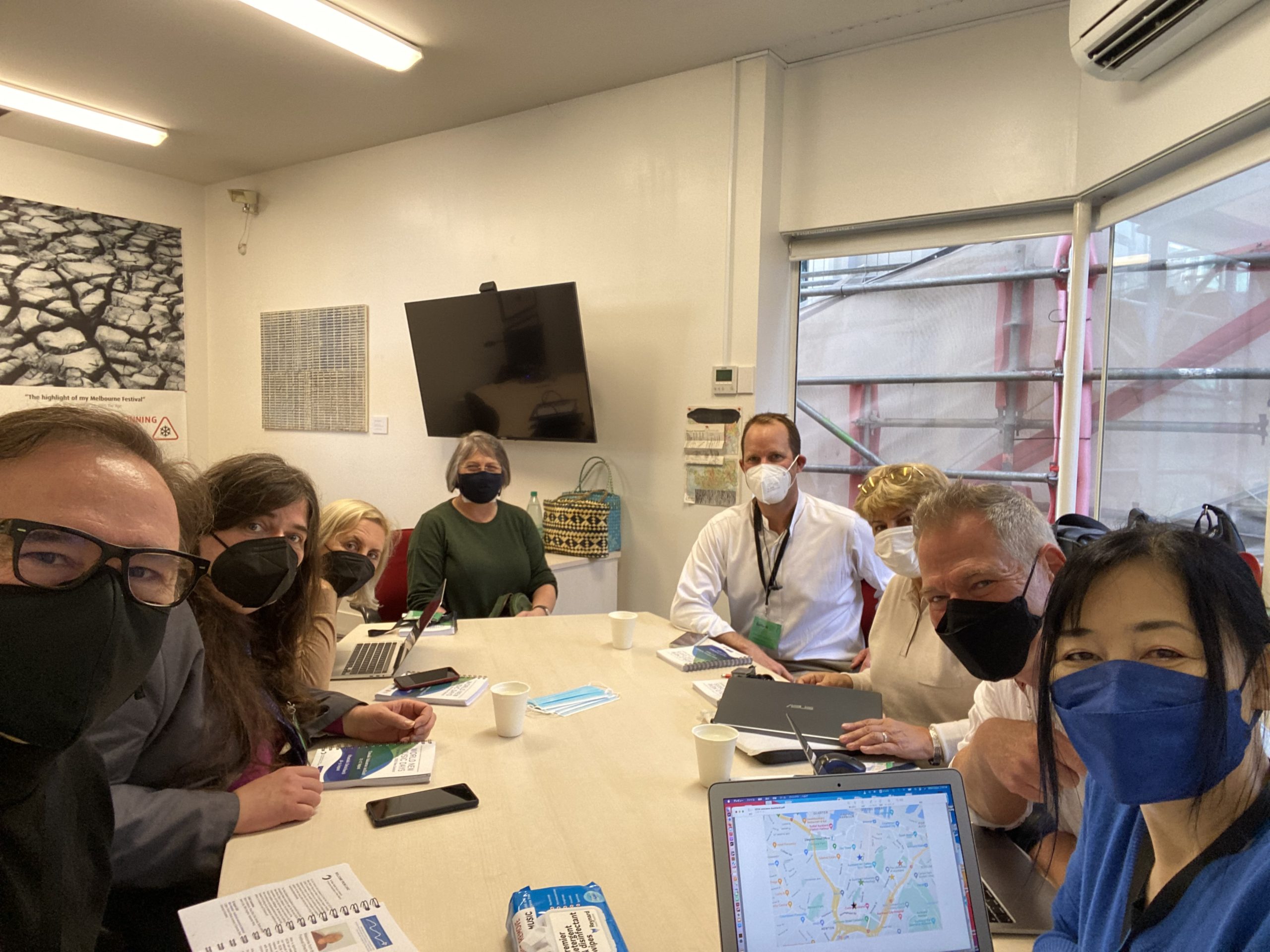

The ISCM Executive Committee met in all day meetings during the weekend before the 2022 World New Music Days began. (Pictured left to right are David Pay, FJO, Oľga Smetanová, Wolfgang Renzl, Irina Hasnaş, George Kentros, and Tomoko Fukui.)
In both cities where the festival took place, before any of the concerts there was a formal welcome (Mihi whakatau) featuring speeches and music from members of the local Māori community, the indigenous people who have inhabited Aotearoa New Zealand long before the en masse arrival of British settlers in the early 19th century and the Māori still make up approximately 16.5% of the country’s population. It was thrilling to hear live performances by Māori musicians on taonga pūoro (the traditional musical instruments of the Māori which have only been revived in recent decades), particularly (and, for a contemporary music festival, very appropriately) the blaring tone clusters that resulted from the simultaneous blowing of pūkaea and pūtātara, trumpet-like instruments made from wood and conch shells respectively, during the first of these welcomes which took place in the courtyard outside the School of Music at the University of Auckland. Admittedly, though, it was somewhat frustrating to listen to the speeches in Māori which were mostly left untranslated. But the solution to that is to learn the language one day! (I must point out that NZ’s overall embrace of Māori heritage and its attempt at establishing a bicultural society is extremely impressive and it has gone well beyond what I previously witnessed when I visited Wellington back in 2007. That said, apart from a few exciting compositions by composers of Māori heritage, such as Takarei Komene, whose 2019 Ngā Roimata o te Tūrama for unaccompanied mixed chorus and whistling was a highlight of a performance by the Auckland Chamber Choir, members of the Māori community did not seem to be part of the “contemporary music” scene in New Zealand. It should be pointed out, however, that the composers from New Zealand whose music was featured on the festival come from extremely diverse cultural backgrounds, ranging from Greece to East Asia.)
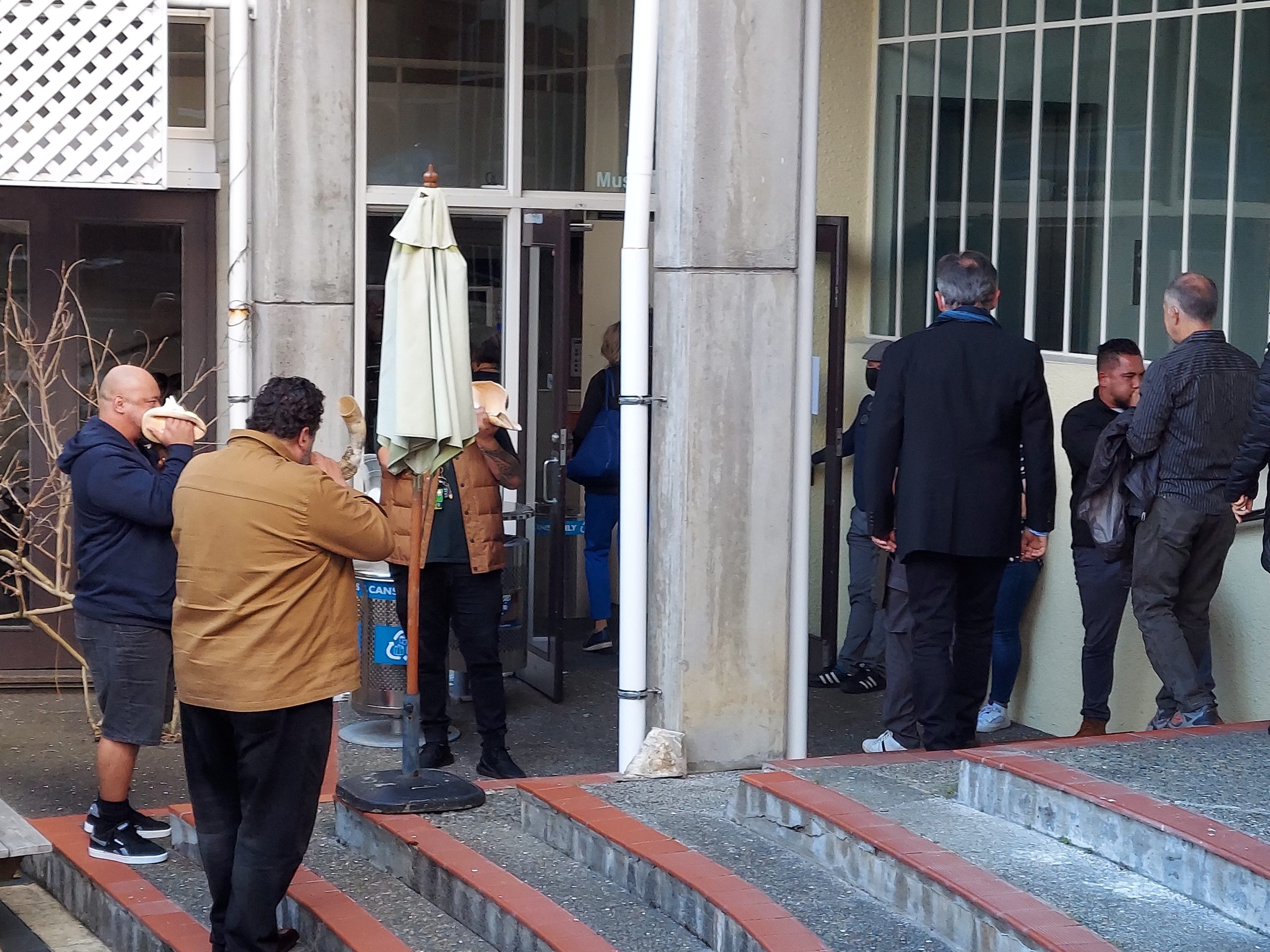

Here are the Māori musicians who greeted all of the ISCM delegates with marvelous tone clusters on taonga pūoro.
The first two concerts of the festival were devoted to music involving electronics. Seven fixed media works (two involving video as well as audio) were presented at the first one, in Auckland’s Audio Foundation, a sub-basement venue located in a neighborhood that is a steep walk from the University. One of the two works involving a video element was Lithuanian composer Albertas Navickas‘s fascinating Silences (2016), which featured fragments of footage of an older woman speaking accompanied by a pre-recorded ensemble which re-enforced the pitch content of her words (a la Scott Johnson’s John Somebody or Steve Reich’s Different Trains). The other was White Heron Dance, a haunting 2017 studio piece by American electronic music pioneer Alice Shields, accompanied by abstract animation (created by Thomas Barratt), which was submitted for inclusion in the festival by the Roger Shapiro Fund for New Music. It was a challenge to distinguish the other pieces since they were not clearly identified during the presentation, which perhaps was part of the gestalt of this very DIY space, but it was nevertheless somewhat frustrating. The second concert, back at the University, involved live electronics and included two works from composers based in the United States: In the Middle of the Room, Jeff Morris‘s 2017 audio-video manipulation of a song by Elisabeth Blair, submitted by ISCM’s Full Associate Member, based at Stephen F. Austin State University, which promotes the music of Texas-based composers; and PS Quartet No. 1, also from 2017, by Korean-born, Michigan-based composer Joo Won Park, in which four performers manipulate audio and video via PlayStation controllers–which was very entertaining both to see and hear. Full disclosure: the latter was the piece among six submitted by New Music USA (it was funded by a Project Grant) which was chosen for performance in the festival. (All ISCM member organizations can submit up to six pieces for consideration in each year’s WNMD and if the submissions are in at least 4 different instrumentation categories, the festival must perform one of them.)
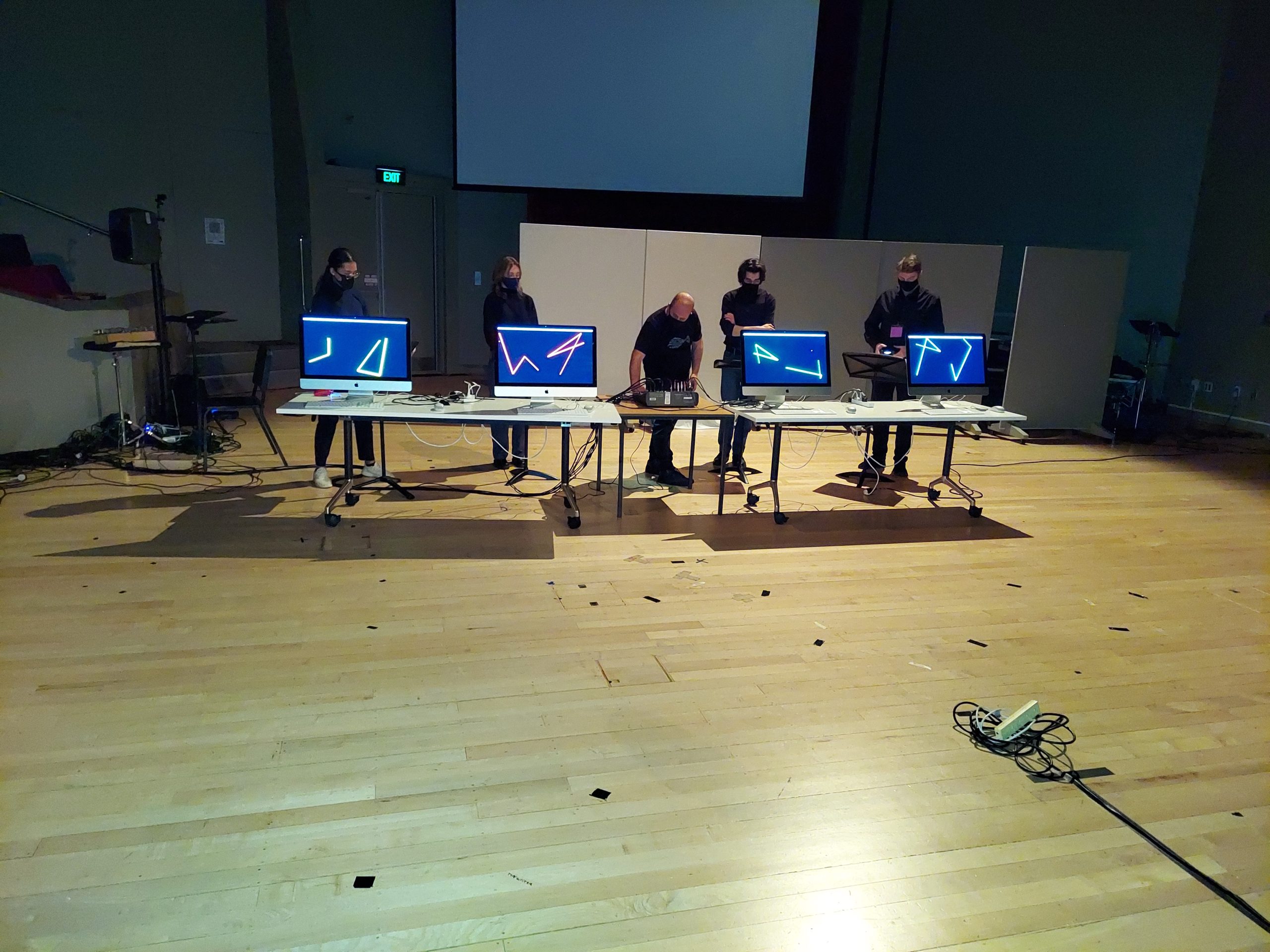

An action shot from the performance of Joo Won Park’s PS Quartet No. 1 at the University of Auckland during the 2022 ISCM World New Music Days.
On the second day of the festival there were two concerts, both at the University of Auckland. The first was a tour de force afternoon recital by percussionist Justin DeHart, a transplant to New Zealand who originally hails from Sacramento, California. In a group of seven pieces from Canada, Portugal, and New Zealand, he demonstrated the extraordinary range of sounds that can be made by just one person striking many different kinds of objects (though at times the sounds he made were enhanced by pre-recorded electronics). The evening concert was devoted to mostly unaccompanied choral works (for one, a harp was added) performed by the aforementioned Auckland Chamber Choir, a group based at the University. The concert opened with the inventive and challenging Sonata form denatured prose (2014) by Swedish-born Norwegian-based composer Maja Linderoth (b. 1989), who was named the winner of the ISCM Young Composer Award at the end of the festival; the first time a female composer had received the award since 2011.
The next day the ISCM delegates travelled to the West Auckland suburb of Titirangi for a concert, again devoted to electronic music, in the Te Uru Waitakere Contemporary Gallery. Lukas Ligeti, an Austrian-born composer who currently divides his time between Florida and Johannesburg, South Africa, performed his Labyrinth of Stars: The Far Southeast (2014), an improvisatory solo for the Donald Buchla-designed marimba lumina. The material for the piece is derived from the composer’s earlier concerto for marimba lumina and orchestra titled Labyrinth of Clouds. In his prefatory comments, Ligeti stated that this new version of the music was inspired by his seeing stars that are visible in this part of the world which are not visible in the Northern Hemisphere and the resultant music juxtaposed a series of diatonic ostinatos with some surprising chromatic intrusions. (I was hoping to see some of those stars, too, but most of the evenings I was there were cloudy, plus most of the time I was too close to city lights to be able to appreciate them.) That concert also featured Interdependencies (2018), a trippy live manipulation of eight interconnected tone generators by Danish composer Christian Skjødt which he said was just part one of a work that is twice as long; I’m eager to hear the rest of it one day. Unfortunately, because I failed to sign up for it in time, I missed Polish composer Mikolaj Laskowski‘s 2018 Deep Relaxation No. 4: Self-Care, an audience participatory piece involving sound objects and yoga mats that was presented twice but was limited to just 12 attendees each time.

While I never saw many stars in NZ, I did see this amazing tree in a park while walking from my hotel to the University of Auckland for ISCM meetings and concerts.
Later in the week, Polish-born New Zealand-based pianist Gabriela Glapska gave a very convincing recital comprised of nine works from eight countries, the most intriguing of which, at least for me, were three selections from Japanese composer Matoharu Kawashima‘s 2017 Action Music, in particular the last one in which the pianist mimics the famous opening of Tchaikovsky’s overplayed first piano concerto, ultimately closing the lid and continuing to play. I was also very taken with a duo recital by violinist/violist Andrew Beer and pianist Sarah Watkins at the hip Loft Q Theatre on Auckland’s busy Queen Street. Everything they played they turned into something extraordinary, but I really loved the brave beauty of Canadian composer Rodney Sharman‘s 2016 viola/piano duo Gratitude and Swiss composer Esther Flückiger‘s often jazzy 2017 Guarda i lumi for violin and piano and will want to hear both works again many times. (Luckily three of the NZ pieces featured on the program were on a CD of the duo I bought the last night of the festival, though I was already familiar with the 2011 miniature Tōrua by Gillian Whitehead, one of NZ’s most prominent composers, since it was one of the Encore Pieces commissioned and recorded by Hilary Hahn.)
I skipped the concluding Auckland event, a screening of a virtual concert by the Australian new music ensemble ELISION who were originally scheduled to participate in person before COVID-related travel restrictions threw a monkey wrench into the plan. But since they plan to post all their virtual performances to their YouTube channel, I hope to catch up with it when they do. Unfortunately the few other programs I wound up missing for a variety of reasons, some having to do with the complexities of navigating Auckland’s challengingly hilly terrain, were mostly not streamed and archived online. After a couple of years of virtual performances becoming a lifeline to musical experiences with the concurrent benefit of these concerts being able to attract audiences from all over world who otherwise could not have experienced them, it seems a shame not to set up even a smartphone (many of which have better audio and video reproduction capabilities than some so-called professional camcorders from 20 years ago) to preserve all performances and make them available to as many people as possible.

The days and nights were pretty tightly packed with meetings and concerts, but there was a gap of a couple of hours one morning so of course I went shopping for LPs and CDs at Penny Lane Records, which thankfully opens quite early.
Although the Festival program in Christchurch lasted a mere four days, it seems like there were twice as many concerts. This is because in addition to concerts featuring repertoire selected from ISCM submissions, there were also concerts devoted to repertoire chosen from the member organizations in the Asian Composers League. It’s far too much music to write about here in a way that won’t seem completely overwhelming, but I would like to call attention to a few things that left a lasting impression.
The Christchurch Youth Orchestra played a very short concert (only about 37 minutes) consisting of five works. Still it was nice to see and hear such a group performing on an important international music festival in front of an audience of people from all over the world and two of the works–Ogham (2018) by Irish composer Ryan Molloy and Distant Lights (2017) by Hong Kong composer Richard Tsang–contained some really exciting orchestration that I’d love to study in greater detail. Another of the pieces, Surcos a la tierra by Chilean composer René Silva, would be a big hit at The Midwest Clinic if Silva were to rearrange it for wind band. Two of the nation’s leading chamber music groups, the New Zealand String Quartet and the NZTrio, offered very wide ranging concert programs. The former, which took place in the 19th century Great Hall in Christchurch’s historic Arts Centre, a real time portal, included an intense 2015 quartet, inside voice, by Kurt Rohde, submitted by ISCM Full Associate member Florida International University, which brought everyone back into modern times. The latter concert, which took place in a posh new venue called The Piano, which was built since the massive 2011 Earthquake, did not include any American pieces, but British composer Joe Cutler‘s clever 2016 McNulty was inspired by the American TV drama series The Wire. Other works on the program included the very effective ACL-commissioned Elehiya Para sa mga Biktima ng Masaker sa Maguindanao (Elegy for the Victims of the Maguindanao Massacre) by Philippine composer Ryle Custodio, winner of the ACL’s 2018 Young Composer Prize, and the rhythmically intriguing Der Tanz by NZ composer Tabea Squire, one of the only works on the festival that was composed this year (since most of the programming was carried over from the postponed 2020 festival).
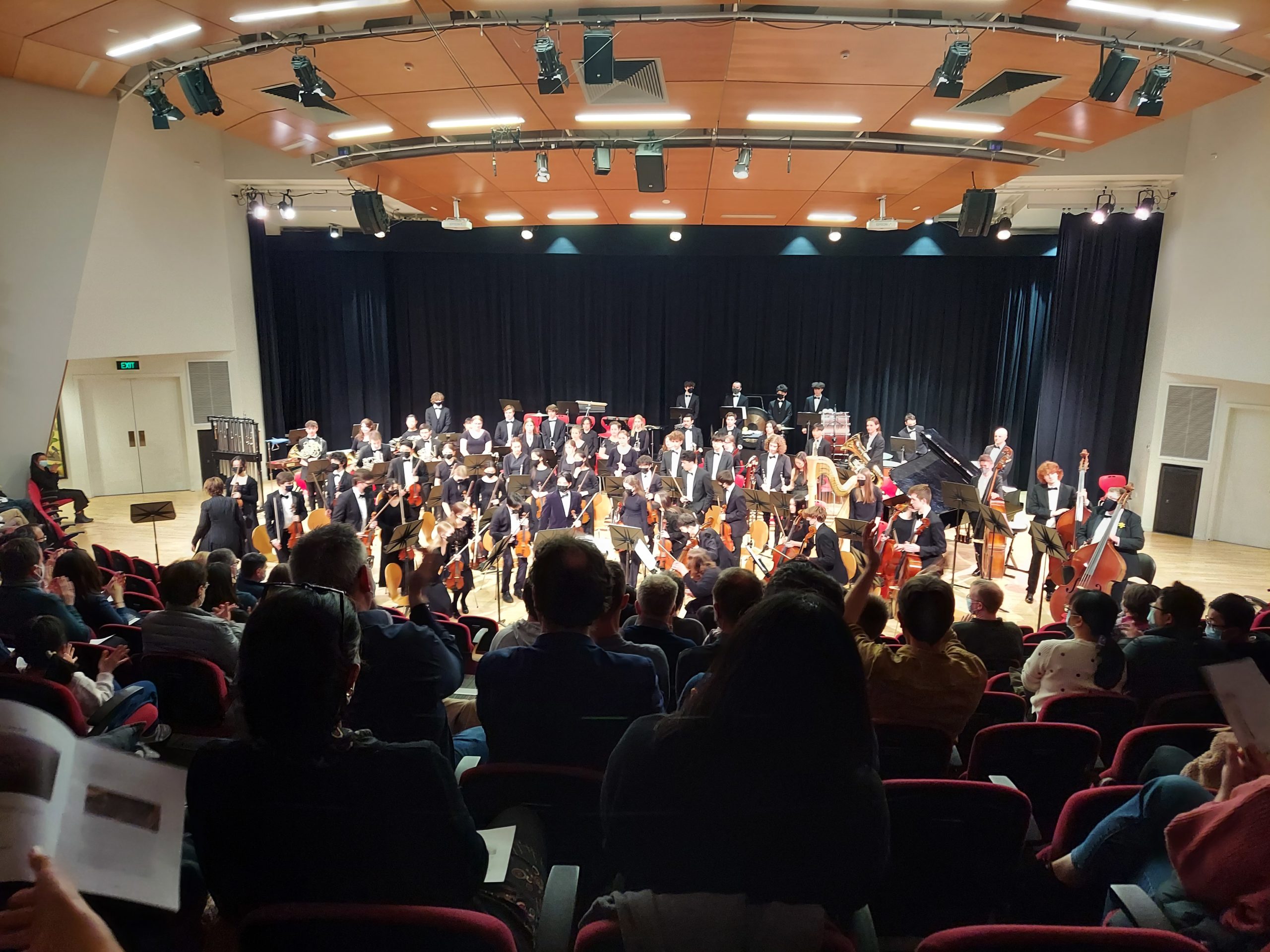

The Christchurch Youth Orchestra conducted by Helen Renaud during their performance at Margaret College’s Charles Luney Auditorium in Christchurch NZ.
Another concert held at The Piano the night before the NZTrio appeared there featured seven very different compositions including the melancholy 2009 What gathers, what lingers by American composer Anna Weesner, another Roger Shapiro Fund submission. A concert at the tiny Recital Room in the University of Canterbury’s Arts Centre, which with two grand pianos seemed like very tight quarters, offered a variety of works which explored inside the piano sonorities. I loved Lauschgut (2019) by German composer Charlotte Seither whom, as luck would have it, was on the panel I moderated at the Beethoven-Haus in Bonn during the public day of the IAMIC Conference (small world). And though it was completed seven years before Putin’s invasion, Forest Cover (2015) by Ukrainian composer Mykola Khshanovskyi, in which the explosive sonorities emanating from the piano are enhanced by pre-recorded and live electronics, sounded extremely timely. Yifan Yang, a piano student at the University of Canterbury, gave a breathtaking account of it.
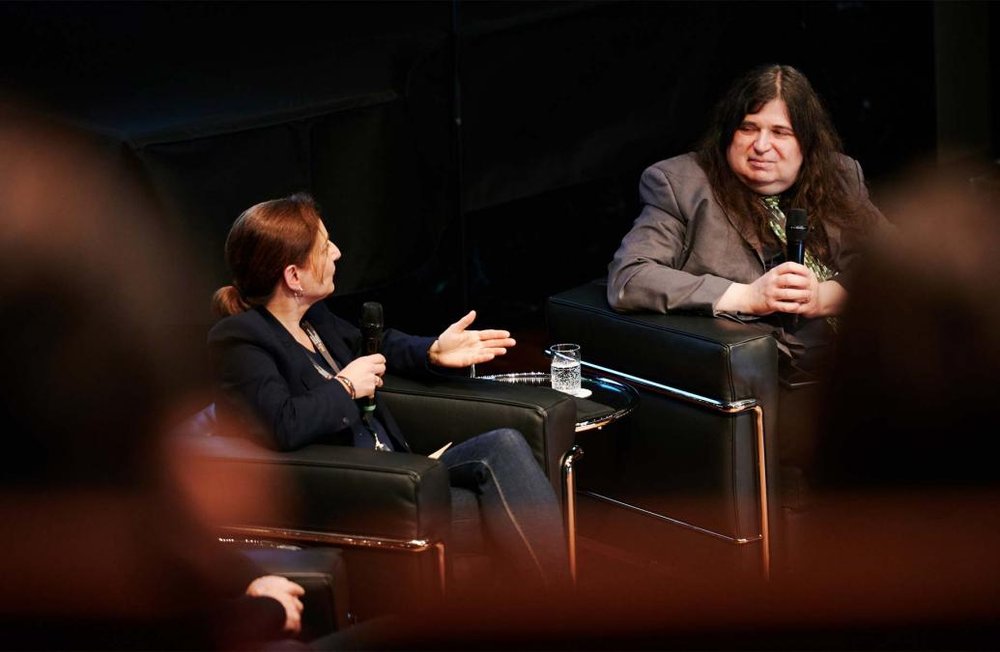

From my panel talk with Charlotte Seither during the public day of the IAMIC Conference at the Beethoven-Haus in Bonn back in May (photo by Nathan Dreessen-of the MIZ)
On the final day there was another concert in the Recital Room devoted to eleven string trios from young composers based in 11 different countries represented within the Asian Composers League. The simultaneously deft and fun handling of numerous extended techniques in bouncing, sliding, spinning (2019) by Thai composer Piyawat Louilarpprasert, who is now based at Cornell, earned him the YCL’s 2022 Young Composer Award, but I was also quite taken with New Zealand composer Glen Downie‘s almost static Two Variations on an Original Chorale (2019). The performances, by two different string trios, felt like a triathlon, particularly when Johnny Chang and Mark Bennett as well as Mark Menzies (who was a ubiquitous onstage presence at the Christchurch concerts) and Rakuto Kurano switched between violin and viola, though at one point Menzies forgot which instrument he was supposed to play. But maybe he was just joking. Either way, it was as compelling visually as it was sonically.
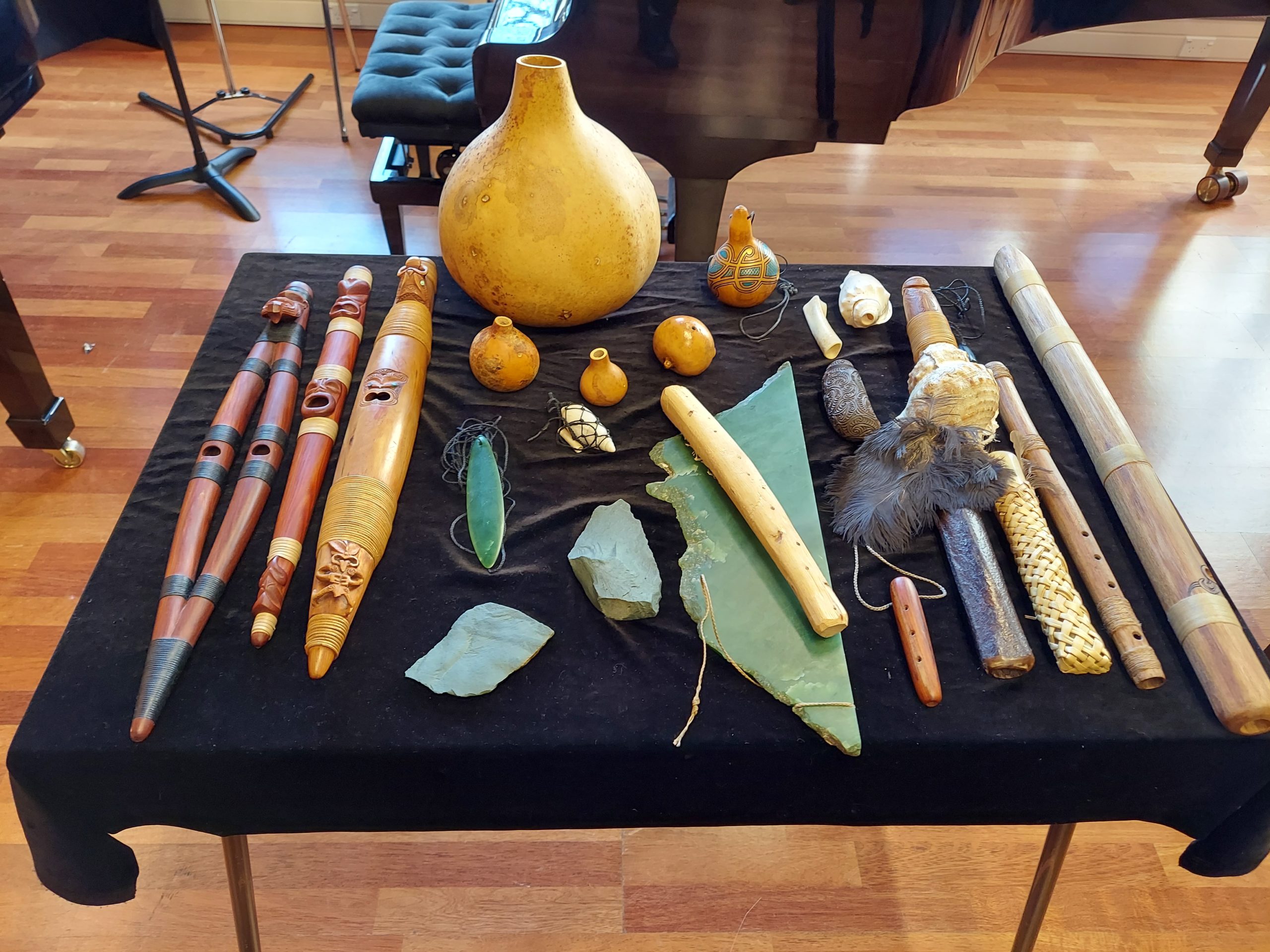

The taonga pūoro that Alistair Frasier performed on during his duo concert with flutist Bridget Douglas.
But the real highlight of the Christchurch events for me was the duo of Alistair Fraser and Bridget Douglas performing on taonga pūoro and Western (silver) flutes, also in the Recital Room. Particularly intriguing were Gareth Farr‘s Silver Stone Wood Bone and Briar Prastiti‘s Terra Firma, both composed in 2019, the latter of which contained passages in which it was sometimes hard to tell which instrument was playing what. It was nevertheless a shame that no members of the Māori community were involved in either the composition or performance of a group of works which were all about bridging the divide between Māori and European cultures. Is it possible that no one in that community has created any music like that yet?

Once upon a time Māori people were forced to recite the line “I will not speak Māori” as part of the Anglicization process during their early schooling. It is something that still haunts the current population of Aotearoa New Zealand.
As I wrote at the onset, I’m still trying to wrap my brain around all of this. In particular, how a festival of contemporary music can truly be representative of what is currently being created all around the world and how such a festival could reach a broader and more diverse audience. Also, are such festivals, which, in the case of the ISCM, have been going on for a century, still feasible in a world that can be shut down by a global pandemic as well as by war and the vagaries of climate change? The ISCM was created a few years after the end of the First World War in an attempt to bring the fractured world together through music, yet in the beginning that world consisted just of countries in Europe plus the United States. As time went on, the ISCM eventually brought in members from South America, Asia, Oceania, and Africa, but 2022 marked only the second time in its history that the festival took place in the Southern Hemisphere. We’re hoping, to mark the centenary of the very first ISCM festival, to meet next year in South Africa, the first time on the African continent, an undertaking which has a great many challenges. But maintaining a festival that takes place every year in a different location in the world might prove to be an even greater challenge.

Of course, the trip back home is as long as the trip there…